Design a Book Cover
Students create a new cover design for a book they are reading to demonstrate comprehension and explore character, plot, setting, symbolism, and conflict.

Task
Students just aren't checking books out of the school library as often anymore. The librarian is hoping to remedy this situation by making the books that are in the library look more appealing!
After finding a book you enjoy, encourage other students to read it by creating a new cover design to entice other students to read it.
Engage
Images can be powerful ways of communicating. People instinctively respond to images based on their personalities, associations, and previous experience. Graphic designers use this instinctive response to visually communicate ideas and information. They work with different tools and mediums to convey a message from a client to a particular audience.
As a class, look at the covers for several books you have read. Does the cover art reflect the content and mood of the book?
Share the librarian's dilemma and ask your students to create new cover jackets for some of their favorite books. Remind them that a book jacket includes:
- A clear title and author name
- A graphic design that reflects the books themes
- A teaser about the plot without giving away the ending
- A review (opinion) about the book
Have students choose a favorite book or one they have read recently.
To help students review what they learned about the book, have them complete a character sketch or character web about the main character. This will help them develop details about the main character, so they communicate information about the character linguistically before trying to do so visually.
You may also find it useful for them to complete organizers that show characters, setting, and events in the beginning, middle, and end or even a more elaborate plot diagram.
Writing the teaser for the back of the cover is also a great place to find ideas for mood and imagery. A book teaser isn't a summary of the story, it is information about the character or events written in a way that hooks a potential reader, similar to how a movie trailer gets a viewer to want to watch a movie.

Download a handout to help elementary or secondary students collect ideas for a book trailer.
Graphic designers need to think about the goal of the images they create. A book cover design should not only give the viewer an idea of the content and mood of the book but should also be eye-catching to encourage students browsing in the library (like customers in a bookstore) to pick up a book they may not be familiar with.
Have students think about the message they want to convey with their book cover and write a short proposal about what they hope their book cover will convey.
For example, in Esperanza Rising, a proposal might look like:
Pam Munoz Ryan’s Esperanza Rising is a story about a well-to-do Mexican girl who had to begin a new life in the farm fields of California. Despite all of her misfortune and hard work, Esperanza Rising is a story about hope for a bright future. The book cover for this story should show her background in Mexico and her hard work in the fields, but the mood should still be uplifting.
Have students share their proposal with a partner who has read their book and discuss the merits of the idea.
- Do you agree with their summary of what should be included on the cover?
- Do you agree with the mood they have chosen?
- What images might they use?
Have students revise and submit their proposal for your review.
Create
Once the students have their proposal written, they should begin looking for potential images they can use in their cover design. Using the descriptive words in their character sketch and cover design worksheets, have them use a digital camera to capture appropriate images and the Internet to explore and download copyright-friendly images from Pics4Learning.
You may also want to give them access to a paint program or art supplies, so they can also create original illustrations and artwork.
Once students have collected all of their image resources, have them use a tool like Wixie to combine them into a front and back cover design or book jacket.

Share
When the cover designs are completed, have students work in small teams to evaluate them. Collect all of the evaluations and then distribute them to the cover designers.
Print the new cover designs and display them around school to promote reading. The librarian may choose to display them in the library to help visiting students connect with literature that interests them.
You could also ask local graphic designers to evaluate student work. Make sure the designers evaluate the work for both design skill and how well the design reflects the content of the book. In other words, bring in designers who love to read!
Assessment
Create a rubric or checklist to help guide student work during research, writing, and final book cover design. Use the Rubric Maker to create a rubric for free. If you use Wixie, use the embedded rubric-making tool. The book cover design templates in Wixie each have a rubric already attached.
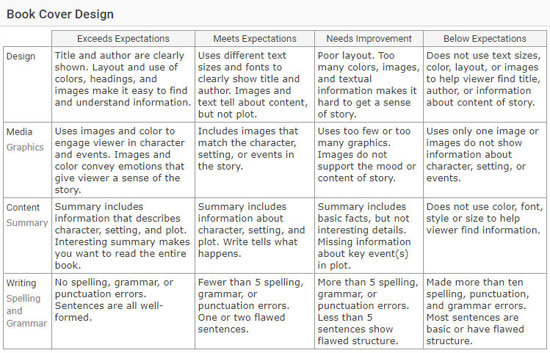
Use the character sketch to evaluate how well students understood the content of the book, as well as their skill at describing the characters and events in the text. Use their cover proposal to evaluate how well they can translate their content research into a design that shares this information visually.
The cover design is a great summative assessment helping you evaluate student's comprehension and skill communicating in a visual medium.
Resources
Powers, Alan. (2001) Front Cover: Great Book Jacket and Cover Design. Mitchell Beazley. ISBN: 1840004215
Powers, Alan. (2003) Children’s Book Covers: Great Book Jacket And Cover Design. Mitchell Beazley. ISBN: 1840006935
Poggenpohl, Sharon Helmer. (1994) Graphic Design: A Career Guide and Education Directory. Watson-Guptill Publications. ISBN: 0823062988
Standards
Common Core Anchor Standards for English Language Arts - Grade 4-10
Writing Standards
Research to Build and Present Knowledge
7. Conduct short as well as more sustained research projects based on focused questions, demonstrating understanding of the subject under investigation.
Speaking and Listening Standards
Presentation of Knowledge and Ideas
5. Make strategic use of digital media and visual displays of data to express information and enhance understanding of presentations.
Reading Standards
Key Ideas and Details
1. Read closely to determine what the text says explicitly and to make logical inferences from it; cite specific textual evidence when writing or speaking to support conclusions drawn from the text.
2. Determine central ideas or themes of a text and analyze their development; summarize the key supporting details and ideas.
10. Read and comprehend complex literary and informational texts independently and proficiently.
Speaking and Listening Standards
Presentation of Knowledge and Ideas
5. Make strategic use of digital media and visual displays of data to express information and enhance understanding of presentations.
Writing Standards
Research to Build and Present Knowledge
7. Conduct short as well as more sustained research projects based on focused questions, demonstrating understanding of the subject under investigation.
ISTE NETS for Students 2016:
6. Creative Communicator
Students communicate clearly and express themselves creatively for a variety of purposes using the platforms, tools, styles, formats and digital media appropriate to their goals. Students:
a. choose the appropriate platforms and tools for meeting the desired objectives of their creation or communication.
b. create original works or responsibly repurpose or remix digital resources into new creations.
d. publish or present content that customizes the message and medium for their intended audiences.